

i stands for the angle of incidence, which is the angle between the incident ray and the normal. The angle between the reflected ray and the perpendicular or normal to the surface is the angle of reflection. The refection angle is measured from a line perpendicular to the reflecting surface. The angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence. The law of reflection states that the principle when the light rays fall on the smooth surface, the angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence, also the incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal to the surface all lie in the same plane. Why the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection? The angles are measured relative to the perpendicular to the surface at the point where the ray strikes the surface. The law of reflection states that the angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence-θr = θi. What is the formula for angle of reflection?
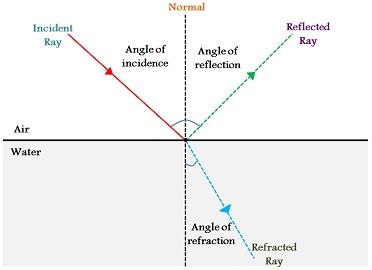
For example, the angle of reflection ∠ NOB is exactly equal to the angle of incidence ∠ AON in the figure given below. The angle of incidence (∠ i) is always equal to the angle of reflection (∠ r), which is given as, ∠ i = ∠ r. Which of the Labelled angles is equal to angle of reflection?ġ. According to the law of reflection, the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. The angle of incidence is the angle between this normal and the incident ray the angle of reflection is the angle between this normal and the reflected ray. Reflection involves a change in direction of the light ray. Is the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection?

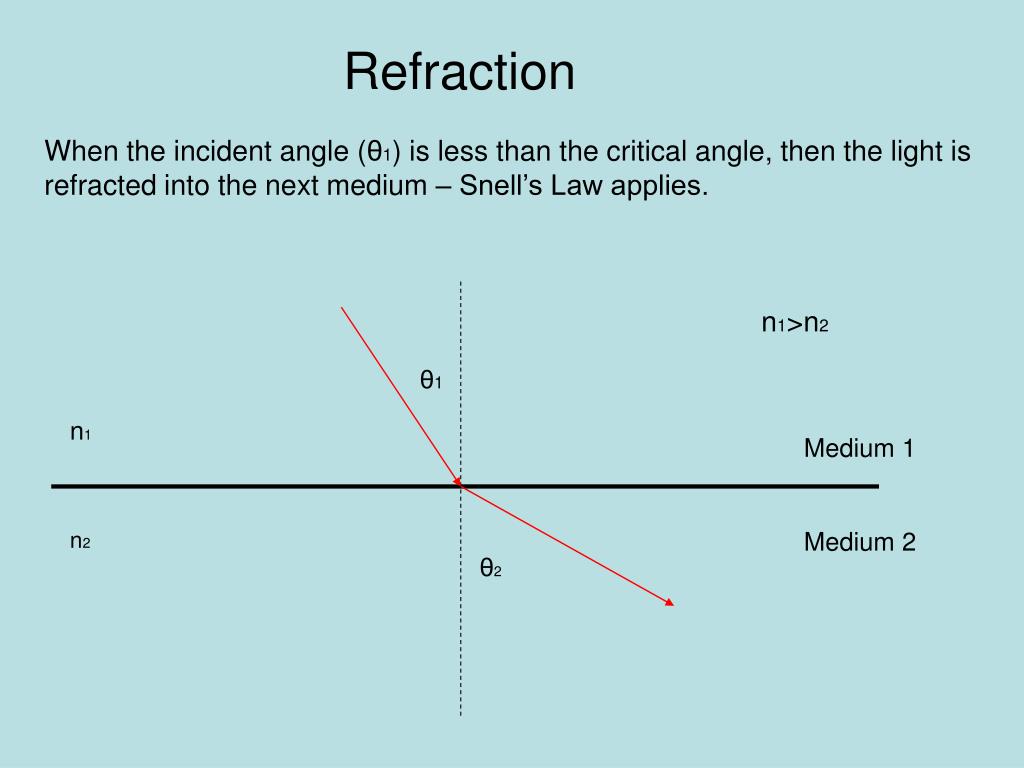
This is called total internal reflection (TIR). When is the critical angle greater than the total internal reflection? The angle of refraction cannot be greater than. When the angle of refraction is equal to, the angle of incidence is called the critical angle. The diagram above shows light incident on a water-air interface. When is the critical angle of light equal to?įor example, this happens when light passes from water to air or from glass to water. At any angle of incidence greater than the critical angle, the light cannot pass through the surface – it is all reflected. Past the critical angle, light is reflected rather than refracted. Angle of incidence more than critical angle. How does the angle of incidence affect the refraction of light?Īs the angle of incidence increases, the angle of refraction gets closer to ninety degrees. – Lelouch Apr 19 ’17 at 15:28 Light is an electromagnetic wave, and as such is governed by the Maxwell equations. There is a special case in which no light is reflected. When the angle of incidence is greater than the critical all light is reflected, why is not all light transmitted when it’s less? That is not always the case. When is the angle of incidence greater than the critical? What is the angle of refraction when the angle of incidence is 30?Īnswer: The angle of refraction is 19.27°. This angle of incidence is known as the critical angle it is the largest angle of incidence for which refraction can still occur. When the angle of incidence in water reaches a certain critical value, the refracted ray lies along the boundary, having an angle of refraction of 90-degrees. The reflected ray will make an angle of 60 degrees (90 – 30 degrees) with the mirror surface. The incident ray will have an angle of reflection of 30 degrees (made with a surface normal to the mirror surface). Since, angle of incidence = angle of reflection = 30 degrees. What is the angle of reflection if the angle of incidence is equal to 30 degrees?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
